Control and Coordination stands with the working together of various body organs in a proper manner to produce suitable reaction to the stimulus.
Stimulus: It is any change in the environment to which an organism responds and reacts. Living organism reacts and respond to various stimuli like heat, light, cold, touch, pressure, etc. Animals and plants both respond to stimuli but in different manner.
Animals
- Nervous System: Nervous system consist of Brain, Spinal Cord and Nerves.
Functions:
Neuron has a cell body called cyton containing a nucleus and cytoplasm. it has several branched structure called Dendrites. These are the points where information is acquired.
Receptors: These are specialized tips of some nerve cells that detect the information from the environment.
Examples:
Phonoreceptors (Inner Ear): hearing/balance of the body.
Photoreceptors (Eyes): visual stimulus.
Thigmoreceptors (Skin): pain touch heat.
Olfactory receptor (Nose): Smell detection
Gustatory Receptors (Tongue): taste detection.
Neuron has a long nerve fibre called Axon which is covered by a protective covering called Myelin sheath. Information travels as an electrical impulse i.e, Nerve impulse through axon.
Nerve end or Terminal Branches : It is a part where electrical signal is converted into chemical message for onward transmission to next neuron by release of neurotransmitters.
Synapse : It is the junction point between two neurons.
Reflex action: Any quick, sudden, immediate response os the body to the certain stimuli that involves spinal cord(not brain) is known as Reflex action. Examples are : withdrawal of hand, Knee Jerk etc.
Reflex arc: It is the pathway through which impulses passes. These arcs are formed in the spinal cord itself, although the information input goes on to reach the brain.
Sensory nerves: These are nerves which carry information from the receptors(sense organs) to the brain and spinal cord.
Motor nerves: These are nerves which carry information from the brain and spinal cord to the effectors(muscles and glands).
Effectors: are the muscles and glands which respond to the
information from the brain and spinal cord through the motor nerves.
Relay Neuron: It is a kind of connector neuron which collects message from the sensory neuron and delivers it to motor neuron after collecting information from spinal cord.
Human Brain:
Brain is the main coordinating centre in the human body. It is protected by the cranium. It is covered by three membranes called meninges filled with a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid which protects the brain from shocks.
The Brain has three main parts: Fore brain, Mid brain and Hind brain.
Fore brain: It consist of the cerebrum and diencephalon. Cerebrum is the seat of memory and intelligence and of sensory centers like hearing, smell and sight.
Diencephalon is the seat for pressure and pain.
Stimulus: It is any change in the environment to which an organism responds and reacts. Living organism reacts and respond to various stimuli like heat, light, cold, touch, pressure, etc. Animals and plants both respond to stimuli but in different manner.
Animals
- Nervous System: Nervous system consist of Brain, Spinal Cord and Nerves.
Functions:
- To receive the information from environment.
- To receive the information from various body parts i.e, stimuli response.
- To act accordingly through muscles and glands.
Neuron has a cell body called cyton containing a nucleus and cytoplasm. it has several branched structure called Dendrites. These are the points where information is acquired.
Receptors: These are specialized tips of some nerve cells that detect the information from the environment.
Examples:
Phonoreceptors (Inner Ear): hearing/balance of the body.
Photoreceptors (Eyes): visual stimulus.
Thigmoreceptors (Skin): pain touch heat.
Olfactory receptor (Nose): Smell detection
Gustatory Receptors (Tongue): taste detection.
Nerve end or Terminal Branches : It is a part where electrical signal is converted into chemical message for onward transmission to next neuron by release of neurotransmitters.
Synapse : It is the junction point between two neurons.
Reflex action: Any quick, sudden, immediate response os the body to the certain stimuli that involves spinal cord(not brain) is known as Reflex action. Examples are : withdrawal of hand, Knee Jerk etc.
Motor nerves: These are nerves which carry information from the brain and spinal cord to the effectors(muscles and glands).
Effectors: are the muscles and glands which respond to the
information from the brain and spinal cord through the motor nerves.
Relay Neuron: It is a kind of connector neuron which collects message from the sensory neuron and delivers it to motor neuron after collecting information from spinal cord.
Human Brain:
Brain is the main coordinating centre in the human body. It is protected by the cranium. It is covered by three membranes called meninges filled with a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid which protects the brain from shocks.
The Brain has three main parts: Fore brain, Mid brain and Hind brain.
Fore brain: It consist of the cerebrum and diencephalon. Cerebrum is the seat of memory and intelligence and of sensory centers like hearing, smell and sight.
Diencephalon is the seat for pressure and pain.
- It is the main thinking par of the brain.
- Controls the voluntary actions.
- Stores information(MEMORY).
- Center associated with HUNGER.
- Receives sensory impulses from various body parts and integrates it.
Hind Brain: It consist of cerebellum, medulla and pons.
- Cerebellum: It controls muscular activities and posture and balance. It also controls precision of voluntary actions.
- Medulla: It controls involuntary actions. Examples: blood pressure, salivation, vomiting etc.
- Pons: It controls involuntary actions and helps in regulation of respiration also.
- Hypothalamus: Helps in chemical coordination.
- Pituitary gland: Helps in secreting hormones.
Peripheral Nervous System:
It facilitates the communication between Central Nervous System and the other parts of the body.
It consist of CRANIAL nerves and SPINAL nerves.
- Cranial Nerves are each of twelve pairs of nerves which arise directly from the brain, not from the spinal cord, and pass through separate apertures in the skull.
- The cranial nerves originate from the brain. Some cranial nerves carry impulses to and from the central nervous system. Some cranial nerves are mixed, while the others are sensory and motor nerves.
- The spinal nerves originate from the spinal cord. All spinal nerves carry impulses to and from the central nervous system. Spinal nerves are mixed nerves.
- In the human there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column.
Spinal cord is enclosed in vertebral column.
How does the Nervous Tissue cause Action?
Nervous Tissue: It is the main component of the two parts of the nervous system; the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system(CNS), and the branching peripheral nerves of the peripheral nervous system(PNS), which regulates and controls bodily functions and activity.
Muscles movements:
- The simplest notion of movement at the cellular level is that muscle cells will move by changing their shape so that they shorten.
- Muscle cells have special proteins that change both their shape and their arrangement in the cell in response to nervous electrical impulses.
- When this happens, new arrangements of these proteins give the muscle cells a shorter form.
Coordination in Plants:
All living things respond to environmental stimuli. Plants also respond to stimuli with the help of chemical compounds secreted by the cells. Plants being living organisms, exhibit some movements.
Directional Movements:
These are also called as tropic movements. Tropic movements are the movements which occur in the direction of the stimulus.
Positive phototropism is seen in shoots which respond by bending towards light.
Negative geotropism is seen in shoots by growing away from the ground.- Roots bend away from light exhibiting negative phototropism.
- They grow towards the ground exhibiting positive geotropism.
- Thigmotropism is the directional growth of a plant part in response to the touch stimulus of an object.
- Hydrotropism is a growth response in which the direction is determined by the stimuli of water.
- Chemotropism is a growth movement of a plant part in response to chemical stimulus. e.g. Growth of pollen tubes towards ovules.
Non-Directional Movements: These are also called as nastic responses. These are exactly the movement of plant parts.
- These movements are independent of growth.
- Plant cells must change their shape for this movement to happen.
- The movement in plants occurs in the direction opposite to the stimulus.
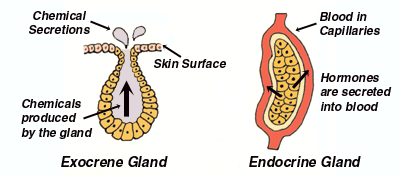
Endocrine gland:
- These are ductless gland.
- They pour secretion directly into the blood.
- They secrete hormones.
- Ex. Thyroid gland.
Exocrine gland:
- They may or may not have ducts(Duct is a tubular bodily canal or passage, especially one for carrying glandular secretion).
- The secretion is poured directly at the site of action.
- They secrete enzymes( Enzymes are biological molecules (proteins) that act as catalysts and help complex reactions occur everywhere in life).
- Ex. Salivary glands, sweat glands.
Plant Hormones:
Are chemical compounds which help to coordinate growth, development and
responses to the environment.
- Auxin:- It is synthesized at shoot tip. It helps in growth of root and shoot tips. These help the plant in growth by cell elongation.
- Gibberellin:- Helps in vegetative growth,growth of the stem, seed germination,bolting and flowering.
- Cytokinins: It promotes cell division,such as fruits and seeds. They also promote the opening of the stomata.
- Abscissic acid: Inhibits growth and cause wilting(falling) of leaves. It is also responsible for the closure of stomata.